
Journal entries typically consist of a date, reference number, debit, credit, and description. Because cash and liabilities both decrease, the equation again remains in balance. If Company A makes a loan payment for $75, the cash account is credited to reflect the outgoing cash, and the liabilities account, which is usually a credit account, is debited to reflect the reduced liability. One asset (cash) increased and one asset (accounts receivable) decreased, with the accounting equation remaining balanced. At the same time, accounts receivable is credited, reflecting a decrease in accounts receivable. With credits, the opposite is true.īy way of example, if Company A receives a $50 payment for an outstanding receivable, the cash account is debited for $50, reflecting increased cash. Going back to the equation above, assets have a default debit balance and on the other side of the equation, liabilities and equity have a default credit balance.ĭebits increase asset and expense accounts and decrease liability and equity accounts. Let's look at double-sided journal entries for a moment.
Generalledger purpose full#
A double-sided journal entry shows the full transaction in all its detail. A cash increase represents a new liability or additional equity. Think of it simply this way: every decrease in cash represents an increase in an expense or asset. The total dollars debited and credited in each entry must always be equal so that the accounting equation stays in balance. If your debits and credits don't balance, you will know you have made a mistake.Įvery entry must consist of at least one debit and one credit but may use more. The double-entry system of accounting ensures that this principle equation always stays in balance. Typically, transactions are organized into these main groupings: assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses, and equity.Ī fundamental principle in accounting is the equation Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity. All debits and credits must balance, so using double-sided entries improves accountability and accuracy. This means that every transaction is recorded as a journal entry in two accounts, with a debit to one and a credit to the other. General ledgers use the double-entry accounting system.

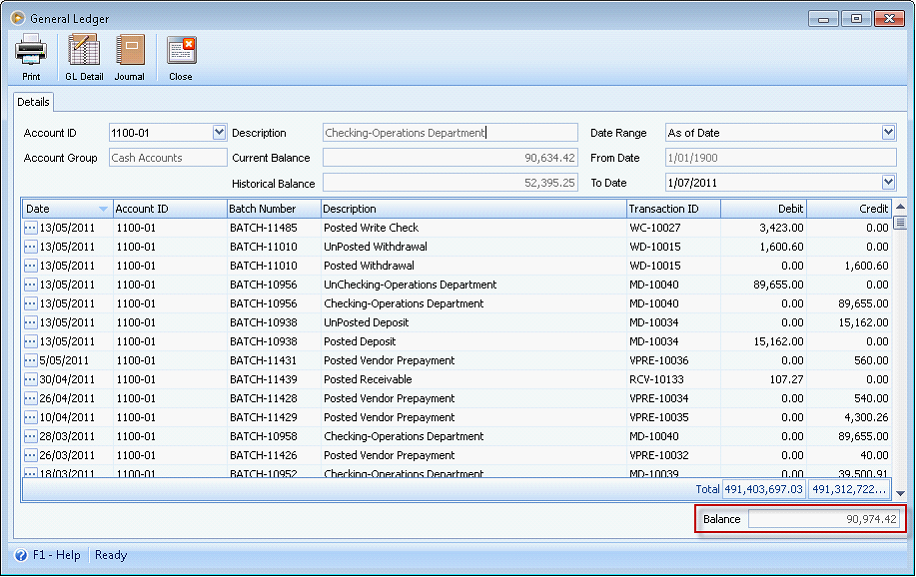
If you've ever had to scramble during tax season, no further explanation is necessary.
Generalledger purpose trial#
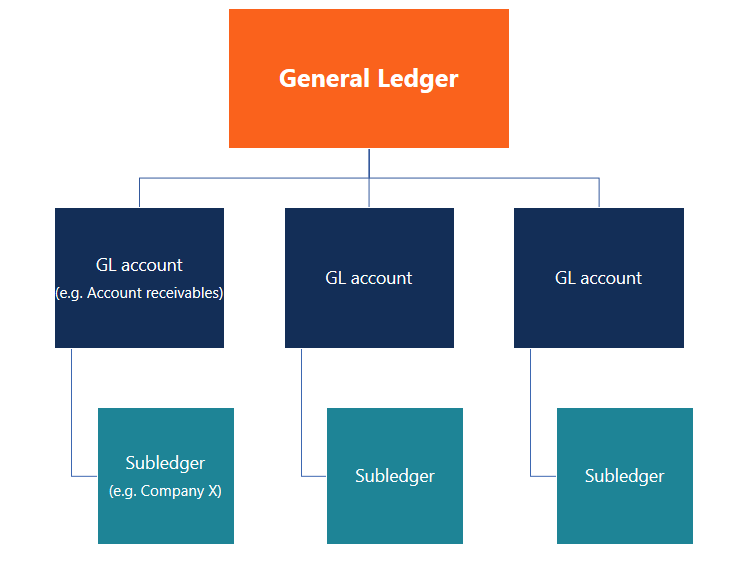
Analyzing changes and trends within the trial balance can yield important information.Ī general ledger is also tremendously helpful when filing taxes since all income and expense transactions are neatly categorized in one location. Comparing transaction data from one time period to the next causes any unusual, erroneous, or fraudulent transactions to stand out. An accurate general ledger is necessary to create accurate financial statements.Ī general ledger can yield information that is not readily evident by reviewing financial statements. Financial statements are a crucial tool in evaluating various measures of overall financial health, including profitability and liquidity. Since each individual journal entry must balance, the sum of all the debits and credits in the trial balance must balance as well.Ī general ledger is helpful for many reasons, each independently important.Ī general ledger is the foundation that financial statements are built upon. A trial balance is a list of every account used and its beginning and ending balance. Financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements all build upon the transaction detail in the general ledger to provide a high-level view of the company's financial health.Īll the detailed transactions in the general ledger combine to form a trial balance. A general ledger keeps a detailed record of every transaction in the life of a company.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
